Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Donor-derived CD7 CAR T cells for pediatric and adult relapsed/refractory T-ALL/LBL: a phase 2 trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Patients with relapsed or refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma continue to have poor outcomes. Pan et al evaluate donor-derived CD7 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells engineered to retain the CD7 molecule intracellularly to prevent fratricide in a study of 55 patients, 38 of whom received CAR T cells derived from their original transplant donor and 17 from a new donor. The authors report promising activity, with 89% of treated patients achieving at least a partial response or better; however, durable remissions occurred only in patients consolidated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, indicating that the value of this therapy is as a bridge to transplant.
Impact of immunochemotherapy regimens on outcomes of patients with primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma in the IELSG37 trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
The first report of this 545-patient randomized International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group (IELSG) trial demonstrated that radiotherapy can be safely omitted in patients with primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) who achieve a complete metabolic response, defined as a Deauville score (DS) of 1–3, following first-line chemoimmunotherapy. In this second analysis, Zucca et al examine the impact of different frontline regimens on patient outcomes and find that treatment with R-CHOP21 (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone, administered every 21 days) is associated with a higher incidence of DS 5 and smaller reductions in metabolic tumor volume after therapy compared with more intensive regimens. Although underpowered for survival comparisons, these findings suggest that R-CHOP21 may be a suboptimal frontline regimen for PMBCL.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
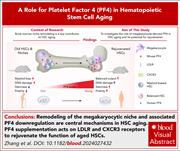
Platelet factor 4 regulates hematopoietic stem cell aging
The role of megakaryocyte and platelet-associated regulation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) is increasingly recognized. Zhang et al provide insight into the aging megakaryocytic niche and its influence on the age-associated decline in HSC and progenitor cell function. The authors demonstrate that remodeling of the megakaryocytic niche and associated platelet factor 4 (PF4) downregulation are central mechanisms driving HSC aging. Notably, PF4 supplementation restores HSC function through low-density lipoprotein receptor and C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 signaling, providing novel insight into strategies to rejuvenate aged HSCs.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
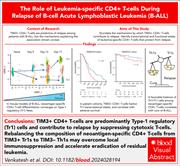
Leukemia escapes immunity by imposing a type 1 regulatory program on neoantigen-specific CD4+ T cells
High frequency of immune checkpoint TIM3+ CD4+ T cells are predictive of relapse in patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), although the mechanisms underlying this association remain unclear. Venkatesh et al use primary B-ALL samples and a novel murine model to show that neoantigen-specific CD4+ T cells can be polarized into type 1 regulatory T cells (Tr1) within the leukemia microenvironment. Reprogramming these neoantigen-specific CD4+ T cells from TIM3+ Tr1 to TIM3- T helper cell phenotypes may counteract local immunosuppression and enhance clearance of residual leukemia. This study reveals a previously underappreciated mechanism of immune evasion in B-ALL and opens new directions for leveraging CD4+ T-cell plasticity in leukemia immunotherapy.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Nanoromidepsin, a polymer nanoparticle of the HDAC inhibitor, improves safety and efficacy in models of T-cell lymphoma
The histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor romidepsin was withdrawn from its indication in peripheral T-cell lymphoma following a negative randomized phase 4 study demonstrating no added benefit of romidepsin-CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) over CHOP alone. Pal et al report the development of nanoromidepsin, a polymer nanoparticle formulation of romidepsin that exhibits improved efficacy, reduced toxicity, and enhanced tumor targeting in preclinical models. These findings may prompt a reevaluation of HDAC inhibition in relapsed or refractory T-cell lymphomas and justify the clinical development of nanoromidepsin for patients with T-cell malignancies.
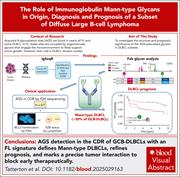
The origin, diagnosis, and prognosis of oligomannose-type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Acquired N-glycosylation sites (AGSs) are present in nearly all follicular lymphomas (FLs) but only in a subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs). In FL, these sites are typically occupied by oligomannose glycans that interact with the microenvironment to promote tumor growth, but their role in DLBCL has remained unclear. Tatterton et al describe an alternative, antigen-independent mechanism of B-cell receptor signaling in DLBCL with AGSs that defines a subset of germinal center B-cell–type DLBCL and serves as an independent marker of poor prognosis. These findings may refine risk stratification in DLBCL and inform therapeutic decision-making.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Impact of ASXL1 at diagnosis in patients with CML receiving frontline potent TKIs: high risk of kinase domain mutations
Additional genomic abnormalities such as ASXL1 mutations present at the time of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) diagnosis influence response to frontline imatinib therapy. Shanmuganathan et al report that ASXL1 mutations confer adverse prognosis in patients with CML, even when treated with more potent tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), including asciminib. Across 4 successive clinical trials, the authors demonstrate that newer TKIs do not overcome the negative impact of cancer gene variants identified at diagnosis. Moreover, the presence of ASXL1 mutations predicts the subsequent development of BCR::ABL1 kinase domain mutations and treatment failure.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Cryo-EM structure of the tissue factor/factor VIIa complex with a factor X mimetic reveals a novel allosteric mechanism
The membrane-bound tissue factor (TF)/factor VIIa (FVIIa) complex initiates blood coagulation by activating factor X (FX). However, structural insights into TF/FVIIa assemblies on membrane surfaces, either alone or in complex with FX, have been lacking. Sedzro et al address this gap by using cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) to solve the structure of the TF/FVIIa complex bound to XK1, a tight-binding analog of the natural substrate FX, on a membrane surface. This study represents a major advance in understanding the intricate interactions of the TF/FVIIa complex and the substrate on membrane surface, which are critical for the initiation and regulation of blood coagulation.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Structure of the membrane-bound complex of tissue factor (purple) and factor VIIa (yellow-orange), bound to a factor X mimetic (XK1, light sea green) and a noninhibitory anti-tissue factor antibody (blue) determined by cryo-electron microscopy. See the article by Sedzro et al on page 2833.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals








Donor-derived CD7 CAR-T in T-ALL/LBL: promise and pitfalls
Clinical Trials & Observations